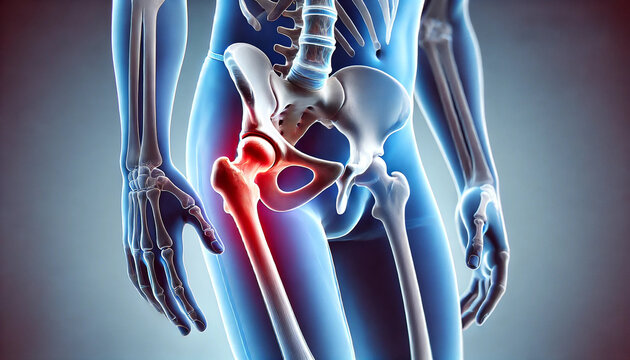
What is Hip Replacement Surgery?
Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a medical procedure designed
to alleviate pain and
improve the function of a severely damaged or deteriorated hip joint. In this surgery,
the damaged sections of
the hip joint are replaced with artificial components made of metal, ceramic, or durable
plastic. These artificial
implants mimic the natural structure and movement of the hip joint, allowing patients to
return to everyday activities
with reduced pain and improved mobility.
This surgery is often recommended for patients experiencing chronic pain or mobility
issues due to conditions such as:
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of joint cartilage and the underlying
bone.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder causing joint
inflammation.
- Hip Fractures: Breaks in the upper portion of the femur.
- Avascular Necrosis: The death of bone tissue due to limited blood
supply.
- Developmental Hip Dysplasia: A condition where the hip joint
doesn’t form properly.
Advantages of Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery is life-changing for many individuals, offering several benefits:
- Significant Pain Relief: Chronic hip pain can make even basic tasks
unbearable. Surgery effectively eliminates this pain, improving overall well-being.
- Improved Mobility and Flexibility: Post-surgery, patients often
regain a full range of motion in their hips, enabling them to walk, climb stairs,
and engage in activities they previously avoided.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Reduced pain and increased mobility allow
patients to live more actively, whether it’s traveling, exercising, or enjoying time
with family and friends.
- Long-Term Effectiveness: Modern implants are designed to last 15-20
years or more, making them a durable solution for hip joint problems.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Recent advancements in surgical
techniques mean smaller incisions, reduced recovery time, and fewer complications.
When Should You Consider Hip Replacement Surgery?
You may need to consider hip replacement surgery if:
- You experience severe hip pain even while resting or during light activities.
- You have difficulty walking, bending, or performing everyday tasks like dressing or
climbing stairs.
- Stiffness in the hip joint restricts your range of motion.
- Conservative treatments like physical therapy, medications, or joint injections no
longer provide relief.
- X-rays show advanced joint damage, such as significant cartilage loss or
bone-on-bone contact.
Types of Hip Replacement Procedures
- Total Hip Replacement (THR): Both the ball (femoral head) and
socket (acetabulum) of the hip joint are replaced.
- Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty): Only the damaged
femoral head is replaced. This is often performed for certain types of hip
fractures.
- Hip Resurfacing: Instead of removing the femoral head, it is
reshaped and capped with a smooth metal covering. This option is typically reserved
for younger, more active patients.
- Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement: Utilizes smaller incisions,
leading to quicker recovery and reduced post-operative discomfort.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after hip replacement surgery varies by individual but typically follows a
structured process:
- Hospital Stay: Most patients stay in the hospital for 1-3 days.
Physical therapy begins within 24 hours to encourage mobility.
- Assistive Devices: Patients may need a walker or crutches initially
to support walking.
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program helps
strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and restore normal movement.
- At-Home Adjustments: Modifying your home to include raised seating,
handrails, and cleared walkways can enhance safety during recovery.
- Full Recovery Timeline: While many patients see improvements within
6 weeks, complete recovery and return to full activity may take up to 6 months.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Hip Health
To ensure the success of your hip replacement and prolong the life of the implant,
consider these lifestyle changes:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional strain on
the hip joint, increasing the risk of implant wear.
- Engage in Low-Impact Exercises: Activities like swimming, walking,
and cycling are ideal for maintaining joint health without overloading the hip.
- Follow Post-Surgical Recommendations: Avoid high-impact activities,
such as running or jumping, to protect your artificial joint.
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and
protein supports overall bone and joint health.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Periodic check-ups with your surgeon ensure
that the implant remains in good condition.
Preventing the Need for Hip Replacement
While some hip issues are unavoidable due to genetics or trauma, others can be prevented
with proactive measures:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise helps maintain joint flexibility and
strengthens the muscles around the hip.
- Practice Proper Posture: Poor posture can lead to uneven wear and
tear on the hip joints.
- Avoid Overuse Injuries: Take breaks during repetitive activities to
reduce strain on the hip.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Shoes with good arch support and cushioning
reduce stress on the hip joints.
Hip replacement surgery is a transformative solution for those struggling with chronic
hip pain and mobility issues.
By relieving pain, improving range of motion, and enhancing overall quality of life,
this procedure empowers patients
to reclaim their independence and lead active lives. If you’re experiencing persistent
hip problems, consult a
specialist to determine whether hip replacement surgery is the right choice for you.
Share This News